In this Article
5 Key Points on Gracilis Flap
1. Workhorse flap for facial reanimation, limb trauma, perineal recon.
2. Pedicle is medial femoral circumflex artery and venae comitantes.
3. Thin muscle in medial thigh located ~2 fingers below adductor longus.
4. Benefits are reliable anatomy with thin volume.
5. Disadvantaged by strength and a variable skin supply.
Gracilis Flap Anatomy
The Gracilis Muscle is 2-3 fingers posterior to the adductor longus. It originates at the pubic symphysis and inserts into the medial condyle of the knee. It is supplied by the medial femoral circumflex system and branch of the obturator nerve.
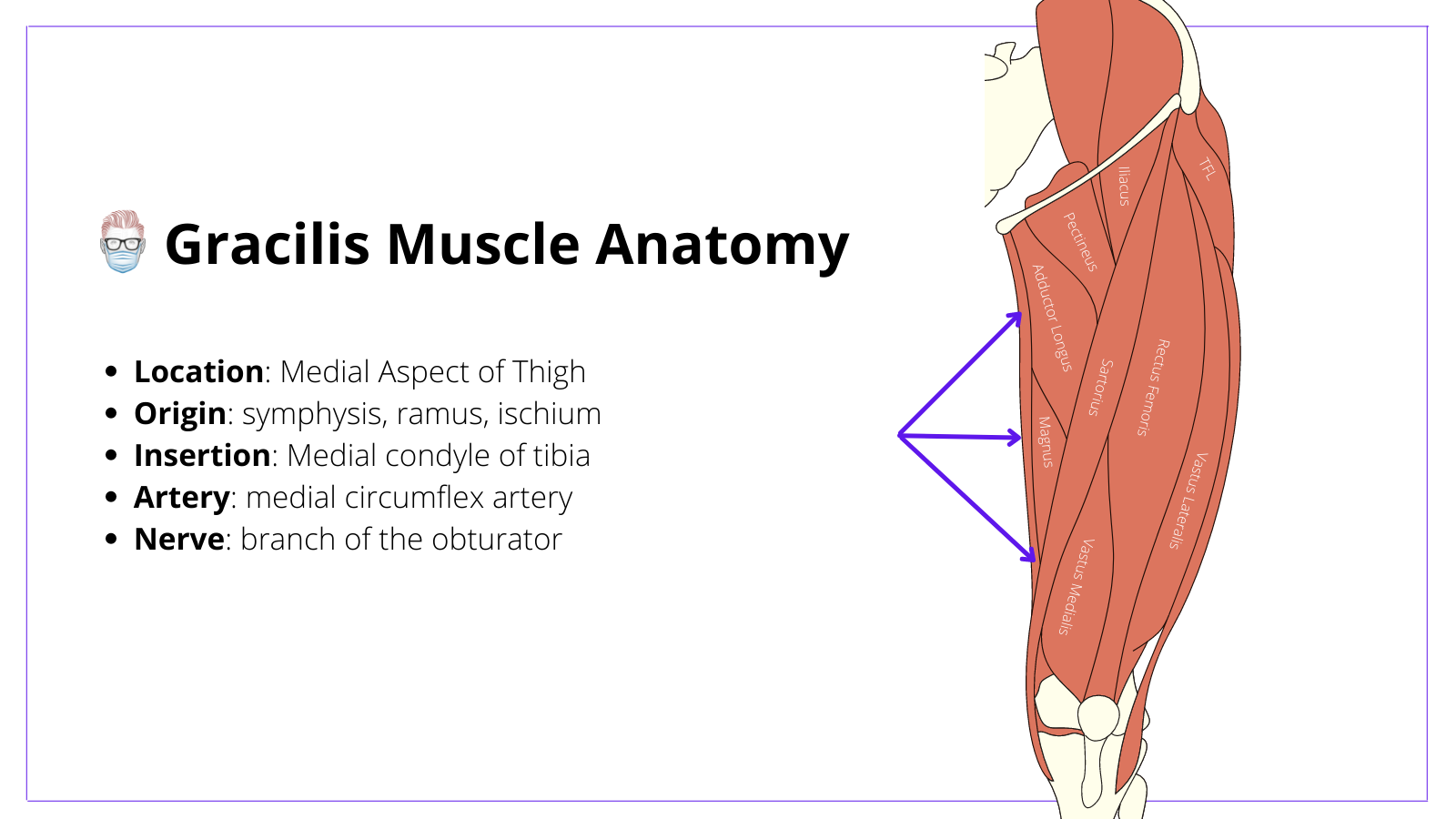
Gracilis Muscle
The gracilis muscle is a flat and thin muscle located superficially in the medial thigh. Here are some key points:
- Location: 2-3 fingers medial and posterior to adductor longus
- Origin is Broad: pubic symphysis, inferior pubic ramus, ischium.
- Insertion is Thin: medial condyle of the tibia and medial tibial surface
- Innervation: branch of obturator nerve
- Function: thigh adduction and knee flexion
- Length: average length is 30cm8
Blood Supply to Gracilis Flap
The gracilis flap is a Mathes and Nahai Type II. It has one dominant and several minor vascular pedicles arising from the medial femoral circumflex (same blood supply as adductor longus).
Pedicle
- Measurements: ~ 7cm long and ~2mm diameter.
- Origin: medial femoral circumflex artery (branch of profunda femoris)
- Course: travels laterally deep to adductor longus on adductor magnus
- Entry: enters muscle ~10cm inferior to pubic tubercle as several branches.
- Minor pedicles are usually proximal & distal (variations do exist1).
- Size: ~2-3cm (larger when directly originating from the deep femoral artery versus when arising from the artery of the adductors). A larger pedicle results in a large volume of gracilis muscle8

Perforators
- Musculocutaneous: more prominent proximally, more variable distally.
- Septocutaneous: direct from pedicle between adductor longus & gracilis.
Veins
- Number: Usually, two venae comitantes travel with the artery.
- Dimensions: ~6cm length and ~2mm diameter
Innervation of Gracilis Muscle
Motor Nerve to Muscle
- This is the anterior branch of the obturator nerve
- It is the motor innervation to the Gracilis Muscle
Sensory Nerve
- This is the medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh
- It is a branch of the obturator nerve
- It courses on the undersurface of the adductor longus muscle as a separate branch, following the course of the motor branch to the gracilis muscle.
How to Perform a Gracilis Flap
Overview
The gracilis flap can be a muscle-only or myocutaneous flap. It is performed under a general anesthetic in a frog-leg position. It is designed relative to the adductor longus. Harvesting requires the identification of gracilis and its pedicle between the adductor muscles.
Frog-leg Position
- Supine
- Thigh abducted
- Knee slightly flexed.
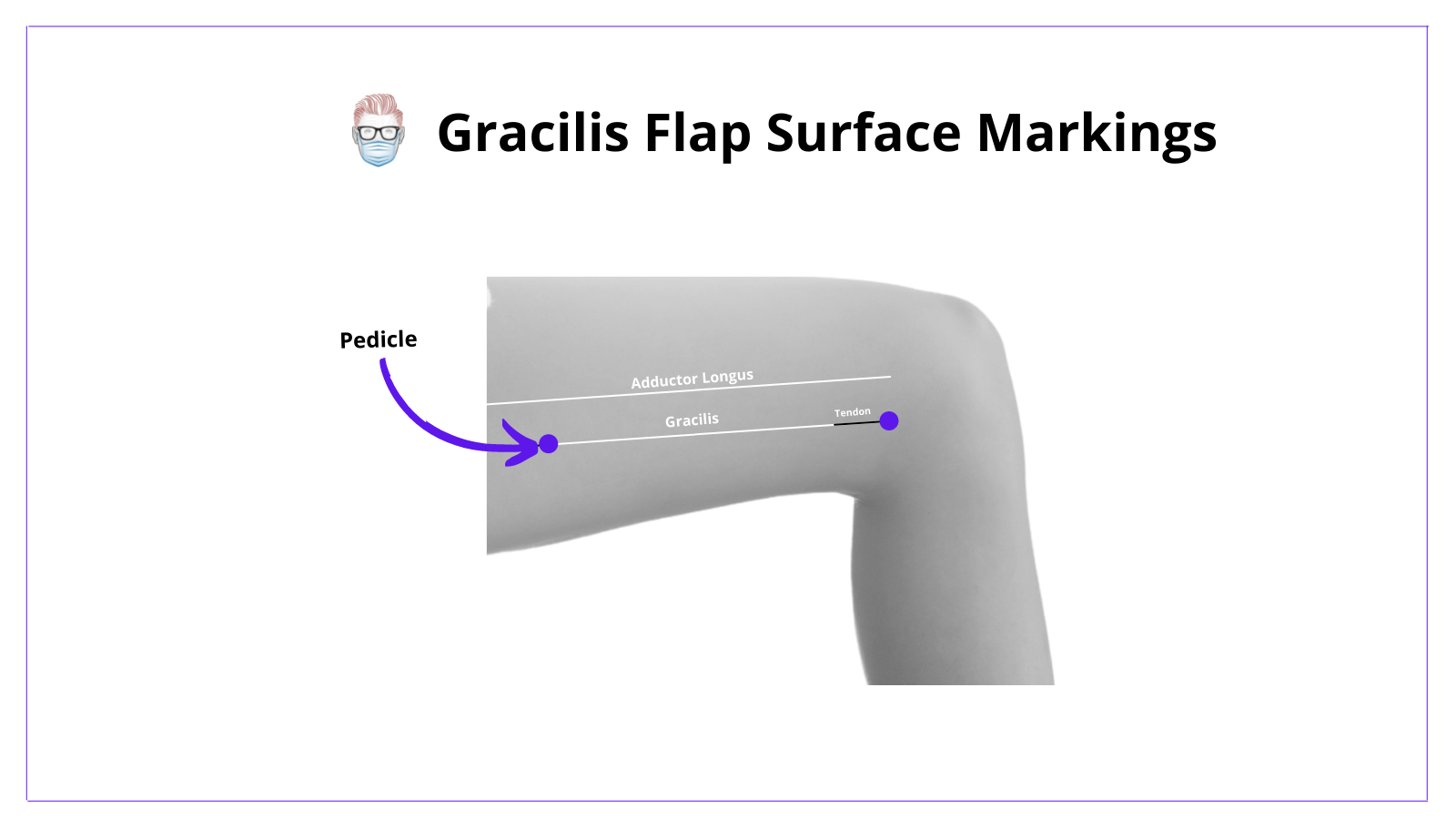
Skin Markings of Gracilis Flap
The following technique should be considered when designing a gracilis flap:
- Identify adductor longus tendon on the proximal aspect of medial thigh
- Measure 2-3 fingers below the adductor longus tendon
- Draw a line along an axis towards the medial tibial condyle
- Mark the expected location of the pedicle ~10cm distal to the groin crease
Myocuntaenous flaps require anterior (lateral) & posterior (medial) incisions.
Steps to Harvesting a Myocutaenous Gracilis Flap
- Incise anteriorly to identify adductor longus.
- Protect the great saphenous vein.
- Retract the adductor longus to visualize pedicle & nerve in the septum.
- Incise posteriorly through subcutaneous tissue to gracilis
- Dissect pedicle b/w adductor longus & magnus until adductor longus branch.
- Mobilize proximally (muscle) and distally (tendon)
- Transect nerve (protect nerve if functional flap)
- Closure in layers with drain.
In-Depth Description
The proximal incision is through fat and muscular fascia. This fascia should be carefully dissected off the muscle to identify the fatty septal junction between the gracilis and adductor longus.
Gentle retraction of these two muscles will reveal the blood supply to the gracilis lying on the adductor magnus.
Dissect and protect this pedicle proximally until you reach the branch of the adductor longus. This usually gives you enough pedicle length.
Release the muscle from it's insertion (and origin in a free flap). The nerve can be divided if the gracilis muscle flap is not planned to be a functional flap.
Indications for Gracilis Flap
The gracilis muscle or musculocutaneous flap is a workhorse flap. It can be used for functional restoration and wound coverage.
Functional Flap (Motor Nerve Protected)
- Facial reanimation
- Anal sphincter reconstruction
Pedicled Flap
- Myocutaneous flap for vagina, perineum, ischium
- Medial Knee Defects (Less Common)
Free Flap
- Lower Limb Trauma
- Breast Reconstruction (Less Common)
- Head and Neck Reconstruction (Less Common)
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Gracilis Flap
- Reproducible anatomy
- Long and reliable pedicle
- Dimensions and volume are ideal for specific areas (e.g facial reanimation)
- Ergonomics allows for two teams (1 preparing, 1 elevation)
- Minimal donor site morbidity or functional issues.
Disadvantages of Gracilis Flap
- Skin blood supply is not constant
- Thin muscle results in less strength.
References
- Mathes SJ, Nahai F. Clinical atlas of muscle and musculocutaneous flaps.
CV Mosby, St Louis, 1979. - Mathes SJ, Nahai F. Classification of the vascular anatomy of muscles: experimental and clinical correlation. Plast Reconstr Surg 1981; 67(2): 177–187
- Chuang DCC, Mardini S, Lin SH, Chen HC. Free proximal gracilis muscle and its skin paddle compound flap transplantation for complex facial paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004; 113: 126–132
- Chwei-Chin Chuang, D. (2009). Gracilis flap. Flaps and Reconstructive Surgery, 397–410.doi:10.1016/b978-0-7216-0519-7.00029-0.
- Azizzadeh B, Pettijohn KJ. The Gracilis Free Flap. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2016 Feb;24(1):47-60. doi: 10.1016/j.fsc.2015.09.002. PMID: 26611701.
- Lyons ME, Goldman JJ. Gracilis Tissue Transfer. 2021 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan–. PMID: 32644472.
- Garcia RM, Ruch DS. Free Flap Functional Muscle Transfers. Hand Clin. 2016 Aug;32(3):397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2016.03.009. PMID: 27387083.
- The clinical role of the gracilis muscle: an example of multidisciplinary collaboration, Decaro, R. PY - 2007/01/01, Pelviperineology


