Summary Card
Overview
Fasciocutaneous flaps — comprising skin, subcutaneous tissue, and deep fascia — offer thin, well-vascularised coverage ideal for reconstructing exposed structures while preserving contour.
Anatomy
Fasciocutaneous flaps use perforator-fed plexuses for reliable perfusion and flexible design — key principles include vascular planning, pattern type, and low donor morbidity
Classification
Cormack & Lamberty classify fasciocutaneous flaps by vascular entry, while Mathes & Nahai focus on pedicle type. Both systems enhance surgical precision and flap survival by defining vascular anatomy.
Clinical Indications
Fasciocutaneous flaps are ideal for covering soft tissue defects where thin, vascularised, and contour-preserving tissue is required — especially in trauma, oncologic, and revision settings.
Fasciocutaneous vs Muscle Flaps
The choice between fasciocutaneous and muscle flaps hinges on wound depth, vascular needs, and functional preservation — fasciocutaneous flaps excel in contour-sensitive areas, while muscle flaps dominate in infection-prone and volumetric reconstructions.
Surgical Technique
Successful fasciocutaneous flap reconstruction depends on meticulous preoperative planning, subfascial dissection preserving perforators, and tension-free inset — followed by diligent vascular monitoring postoperatively.
Complications
Fasciocutaneous flaps are generally safe and effective, but complications such as necrosis, venous congestion, and donor site issues can occur — most often due to vascular compromise, tension, or poor intraoperative handling.
Updated by: Dr Hatan Mortada, Educational Fellow.
Verified by thePlasticsFella ✅
Overview of Fasciocutaneous Flaps
Fasciocutaneous flaps — comprising skin, subcutaneous tissue, and deep fascia — offer thin, well-vascularised coverage ideal for reconstructing exposed structures while preserving contour.
Fasciocutaneous flaps, also called axial flaps, exclude muscle but include skin, fat, and fascia, providing structural and vascular benefits. These flaps have become increasingly valuable in reconstructive surgery due to their versatility, pliability, and dependable perfusion.
The concept and utility of fasciocutaneous flaps have evolved through landmark contributions that advanced both design principles and vascular understanding.
- Pontén (1981): First described fasciocutaneous flaps for lower limb reconstruction. His inclusion of deep fascia extended safe flap dimensions (length-to-width ratio up to 3:1), improving survival.
- Haertsch & Barclay (1981–1982): Demonstrated that fascia preserves longitudinal anastomotic vascular pathways, especially the suprafascial plexus, enhancing perfusion across flap length.
- Cormack & Lamberty (1984): Developed a classification system based on vascular anatomy—random, axial, septocutaneous, and musculocutaneous perforator flaps—standardising flap selection and improving planning.
Pontén’s 1981 fasciocutaneous flap revolutionised reconstruction — offering better contour, less donor-site morbidity, and no muscle sacrifice.
Anatomy of Fasciocutaneous Flaps
Fasciocutaneous flaps use perforator-fed plexuses for reliable perfusion and flexible design — key principles include vascular planning, pattern type, and low donor morbidity
Fasciocutaneous flaps provide consistent soft tissue coverage without compromising muscle, making them valuable in reconstructive surgery. Their effectiveness is rooted in a detailed understanding of vascular anatomy and the strategic use of perforator vessels.
Vascular Plexuses
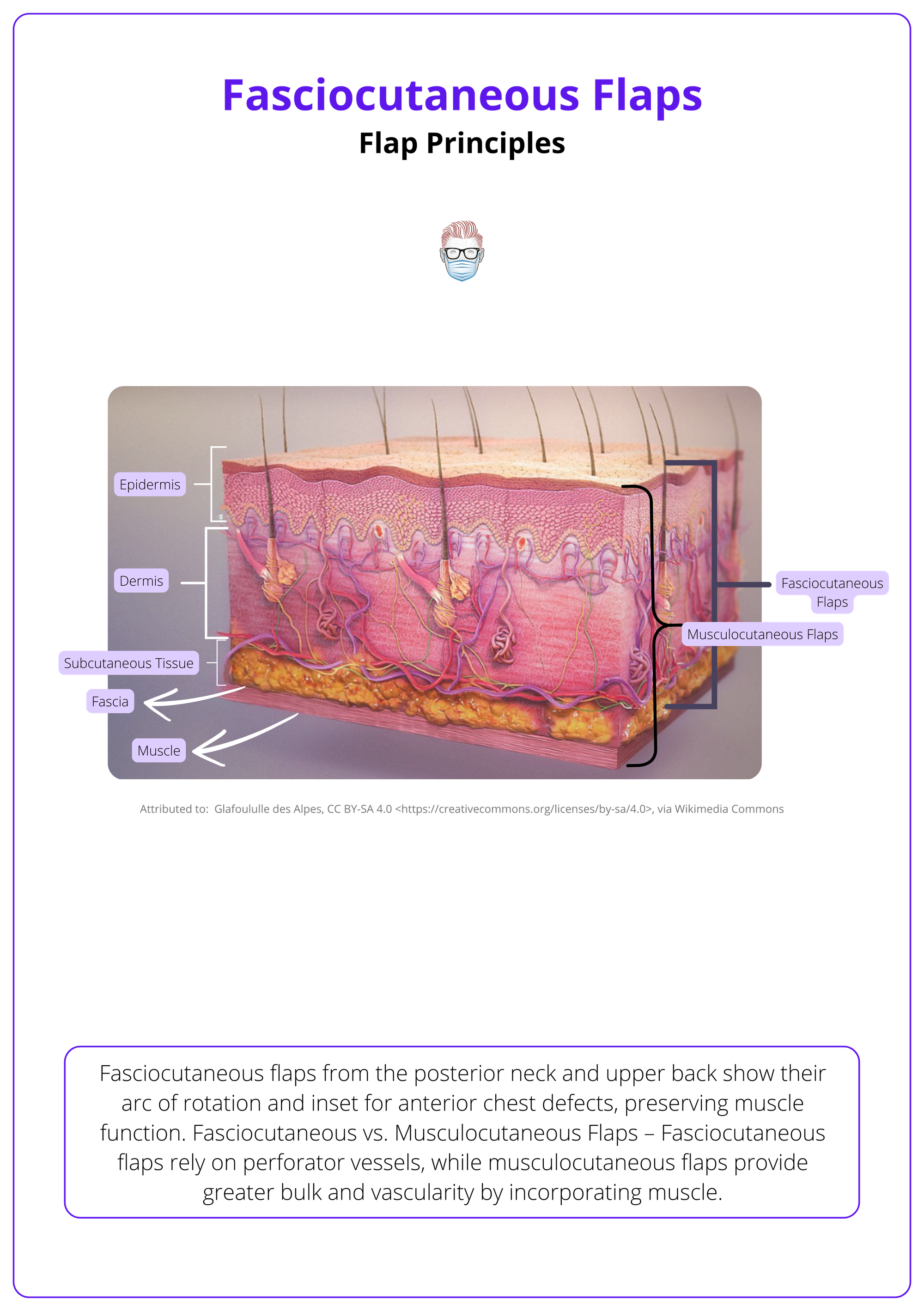
The vascular anatomy of fasciocutaneous flaps is centered around interconnected plexuses fed by perforator arteries that guide flap design and survival.
- Suprafascial Plexus: The primary vascular network that runs above the deep fascia, ensuring robust skin and fascial perfusion.
- Subfascial Plexus: Located between deep fascia and underlying muscle, this layer supports flap viability and links to deeper arterial sources.
- Subdermal & Dermal Plexi: These smaller vessels form a collateral network that further stabilises perfusion, especially in distal or narrow flaps.
- Source Vessels: All plexuses are ultimately fed by perforators branching from main axial arteries, such as the profunda femoris or radial artery, depending on flap location.
The anatomy of fasciocutaneous flaps is illustrated below.
Perforators
The route and origin of perforators influence flap selection, reliability, and dissection complexity.
- Musculocutaneous Perforators: Traverse muscle tissue to reach the fascia and skin, often requiring intramuscular dissection (e.g., thoracodorsal perforator flap).
- Septocutaneous Perforators: Run in intermuscular septa and are easier to dissect; commonly found in limbs (e.g., fibular flap).
- Direct Cutaneous Branches: Arise directly from source arteries without passing through muscle or septa, offering straightforward flap elevation.
The type and consistency of perforators vary by anatomical region, influencing flap reliability and planning.
- Extremities: Dominated by septocutaneous perforators, offering consistent and easy-to-harvest vascular pedicles.
- Trunk: More variable and reliant on musculocutaneous perforators, requiring deeper dissection and more meticulous planning.
- Scalp and Face: Rich in direct cutaneous branches due to superficial arterial networks, allowing thin and mobile flaps.
The fibular flap is a classic example of a fasciocutaneous flap with septocutaneous perforators — surgeons often prefer it for mandibular reconstruction due to its consistent anatomy and dual utility (bone + skin).
Classification of Fasciocutaneous Flaps
Cormack & Lamberty classify fasciocutaneous flaps by vascular entry, while Mathes & Nahai focus on pedicle type. Both systems enhance surgical precision and flap survival by defining vascular anatomy.
Understanding the classification of fasciocutaneous flaps allows surgeons to better predict perfusion patterns, plan dissections, and minimise complications. Two foundational systems — Cormack & Lamberty and Mathes & Nahai — categorise flaps by vascular design, providing critical frameworks for clinical decision-making.
Cormack & Lamberty Classification
This system organises flaps into four types based on how vascular perforators enter and supply the flap, focusing on anatomical blood supply routes (Cormack & Lamberty, 1984).
- Type A – Multiple Perforators at Base
- Supplied by several fasciocutaneous perforators entering the flap base.
Allows for both proximal and distal orientation. - Example: Most lower limb flaps.
- Supplied by several fasciocutaneous perforators entering the flap base.
- Type B – Single Perforator
- Perfused by one dominant perforator, suitable for island or free flap design.
- Example: Scapular flap.
- Type C – Septal-Based with Main Artery
- Vessels enter through a fascial septum; the main artery is included in the flap.
- Example: Radial forearm flap.
- Type D – Composite Flap
- Includes additional components such as bone or muscle with a fasciocutaneous element.
- Example: Osteocutaneous radial forearm flap.Mathes & Nahai Classification (Based on Pedicle Type)
Cormack & Lamberty classification guides where to dissect and whether the main artery must be included.
Mathes & Nahai Classification
This classification categorises flaps based on the type of vascular pedicle that supplies the skin and fascia, useful in determining free vs. pedicled flap design (Mathes & Nahai, 1981).
- Type A – Direct Cutaneous Pedicles
- Supplied directly by branches from an artery to the skin.
- Example: Groin flap, Foucher flap.
- Type B – Septocutaneous Pedicle
- Blood supply reaches the flap via perforators through intermuscular septa.
- Example: Scapular flap, Posterior Interosseous Artery flap.
- Type C – Musculocutaneous Pedicle
- Vascularised by perforators passing through underlying muscle.
- Example: Anterolateral Thigh (ALT) flap.
Mathes & Nahai help determine the vascular reliability, especially for free tissue transfer.
These fasciocutaneous flap classification systems are summarised in the table below.
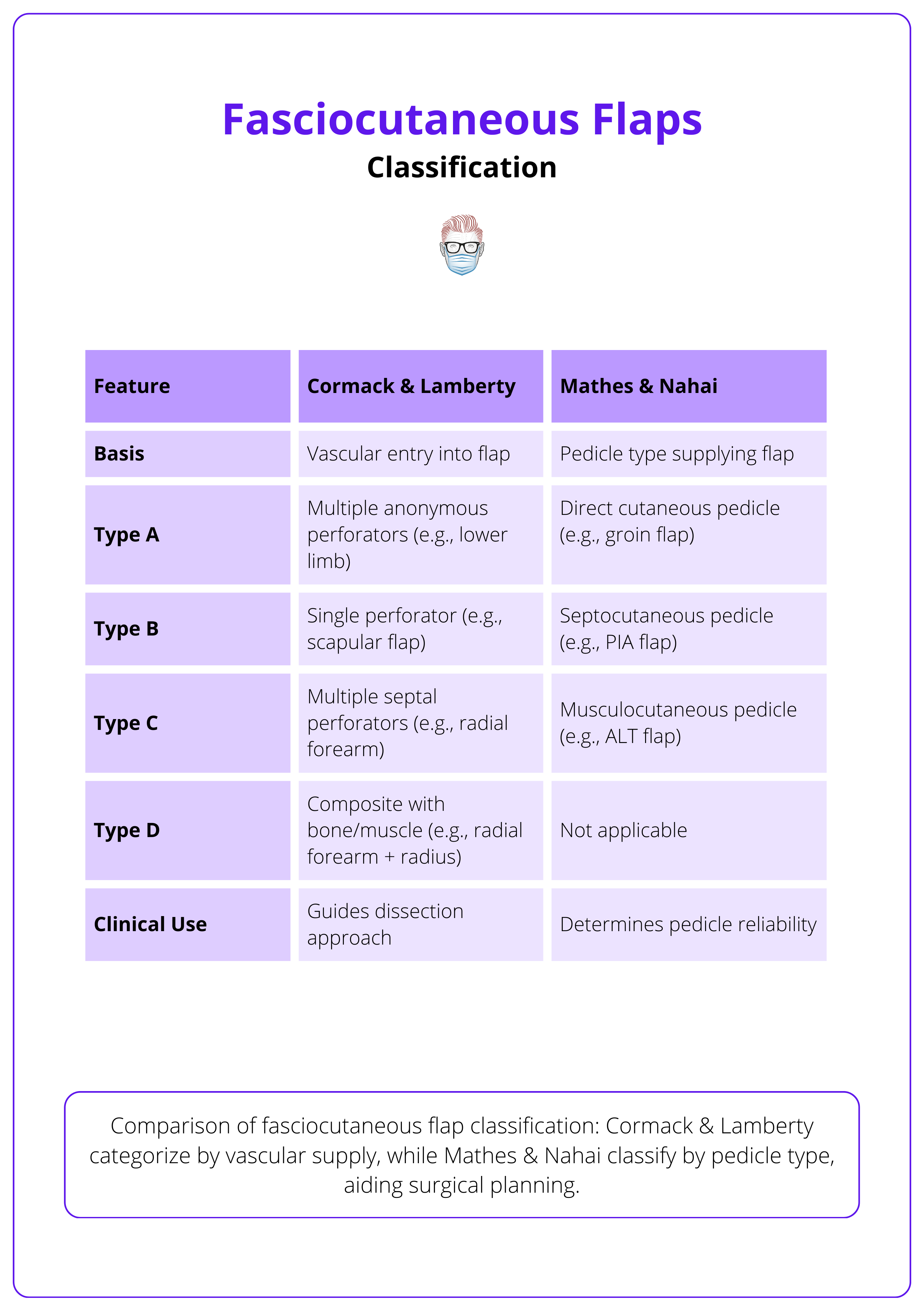
Use Cormack & Lamberty to understand how vessels enter the flap, and Mathes & Nahai to assess pedicle quality for safe elevation and transfer.
Clinical Indications for Fasciocutaneous Flaps
Fasciocutaneous flaps are ideal for covering soft tissue defects where thin, vascularised, and contour-preserving tissue is required — especially in trauma, oncologic, and revision settings.
Fasciocutaneous flaps offer tailored solutions across trauma, oncologic, and salvage scenarios, with demonstrated reliability and versatility.
Trauma Reconstruction
- Covers open fractures, degloving injuries, and burns with tissue that conforms well and preserves joint mobility.
- Useful in both acute trauma and subacute reconstruction stages.
Oncologic Defects
- Effective following tumor excision, particularly in head and neck or extremity cancers (Hanasono, 2014).
- Offers good aesthetic outcomes with minimal donor morbidity.
Chronic Wounds and Pressure Sores
- Preferred for wounds in thin-skinned or high-risk areas like the lower leg and dorsum of the hand (Chiu, 2017).
- Durable yet non-bulky coverage supports long-term healing.
Head, Neck, and Trunk Reconstruction
- Flaps like the forehead or supraclavicular fasciocutaneous flap are ideal for nasal lining or oropharyngeal repair.
- Chosen over muscle flaps where bulk could distort anatomy.
Revision and Salvage Surgery
- Valuable in covering exposed hardware, revising failed flaps, or minimising the need for additional grafts (AlMugaren et al., 2020).
- Their dependable perfusion supports healing in compromised fields
The image below illustrates a forehead fasciocutaneous flap used for nasal reconstruction.
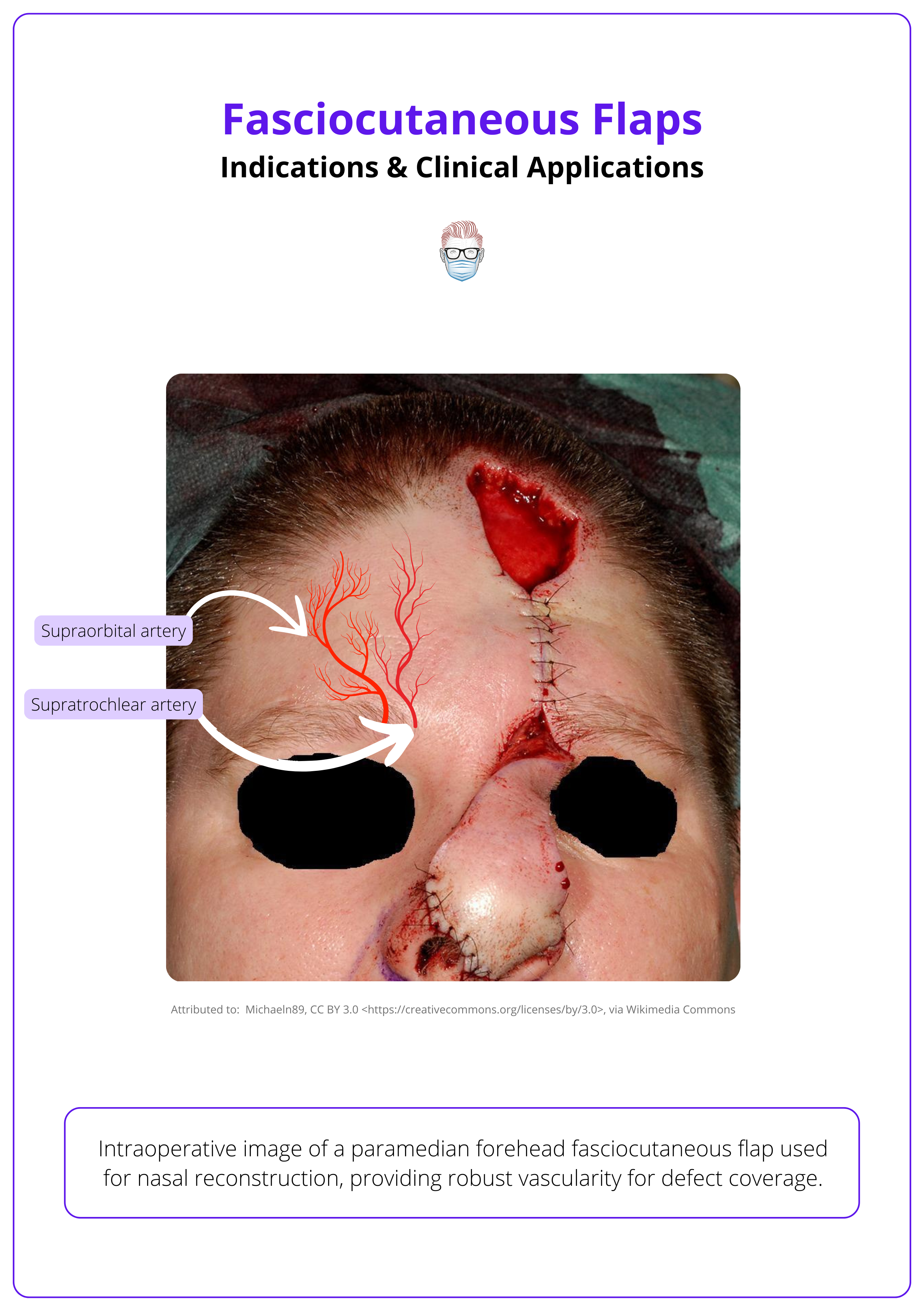
Consider fasciocutaneous flaps for thin-skinned areas. Ideal for lower limb, hand dorsum, nasal lining, and oropharynx, where muscle flaps would be too bulky.
Fasciocutaneous Flaps vs Muscle Flaps
The choice between fasciocutaneous and muscle flaps hinges on wound depth, vascular needs, and functional preservation — fasciocutaneous flaps excel in contour-sensitive areas, while muscle flaps dominate in infection-prone and volumetric reconstructions.
Fasciocutaneous and muscle flaps serve distinct purposes, each tailored to specific clinical demands based on anatomy, perfusion, and the complexity of the defect.
Fasciocutaneous Flaps
Fasciocutaneous flaps provide thin, well-vascularised tissue suitable for restoring contour and function with minimal disruption to underlying musculature.
- Thin and Pliable Coverage Is Required: Ideal for the lower limb, hand dorsum, and facial regions where excessive bulk can impair aesthetics and mobility.
- Muscle Function Must Be Preserved: Useful in the upper and lower limbs where sacrificing muscle would compromise movement or strength.
- Contour Restoration Is a Priority: Their natural conformity makes them the flap of choice in head, neck, and extremity reconstructions.
- Single-Stage Reconstruction Is Preferred: Reduces the need for multiple operations or secondary grafting, accelerating recovery.
Muscle Flaps
Muscle flaps offer robust vascularity and volume, making them effective for complex or infected wounds and for obliterating deep spaces.
- Deep or Irregular Wounds Require Filling: Muscle bulk fills cavities and irregular defects that fasciocutaneous flaps may not adequately address.
- Infection Control Is Crucial: The high perfusion rate in muscle flaps aids in delivering immune cells and antibiotics to contaminated fields.
- Bulk Is Beneficial: Indicated in cases like pressure sores, traumatic tissue loss, or post-oncologic defects where volume restoration is needed.
The key differences between fasciocutaneous and muscle flaps are summarised below.
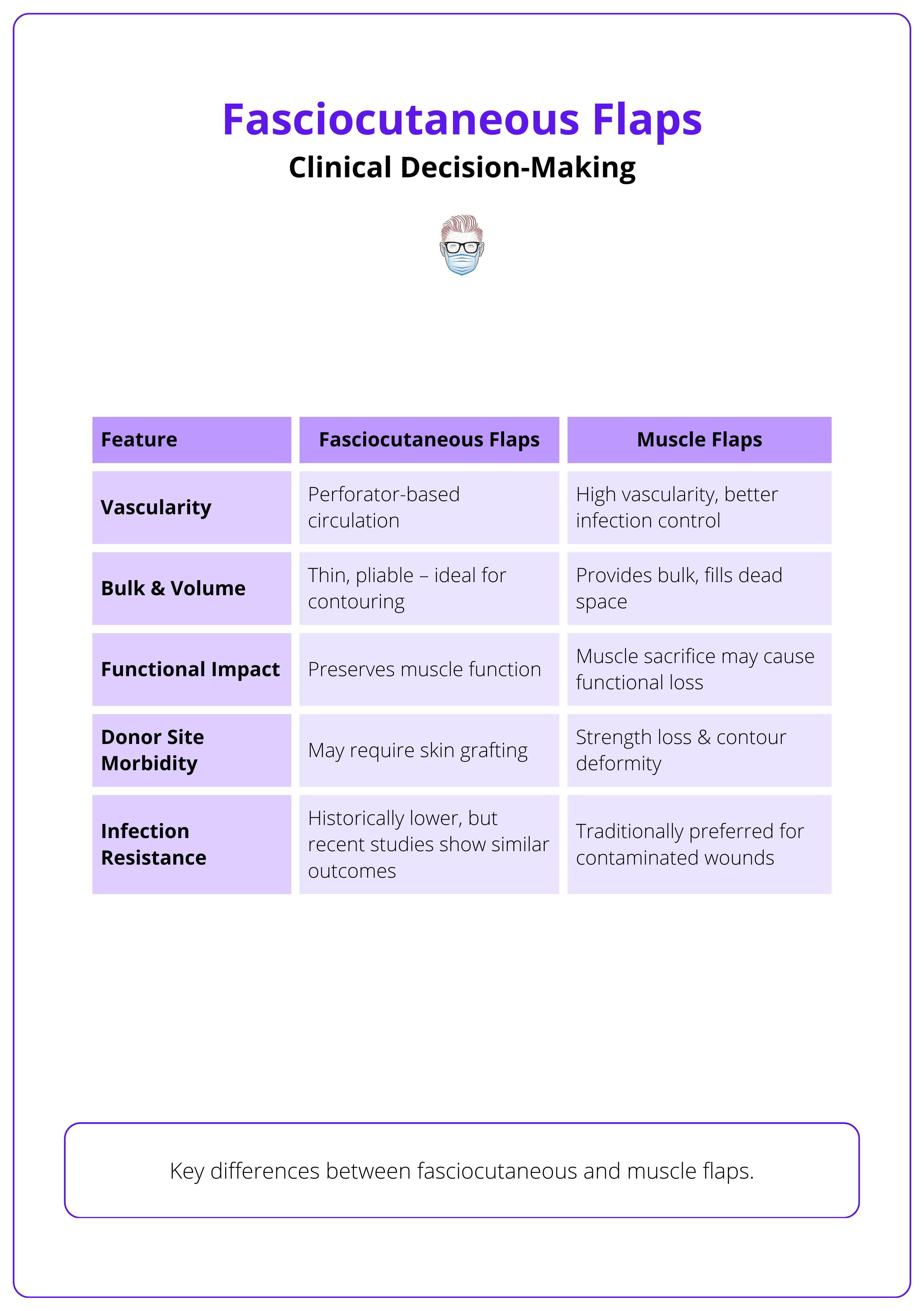
Fasciocutaneous flaps were once considered inferior to muscle flaps for infected wounds due to presumed lower vascularity, but recent evidence shows they offer comparable outcomes (Lee, 2019)
Surgical Technique of Fasciocutaneous Flaps
Successful fasciocutaneous flap reconstruction depends on meticulous preoperative planning, subfascial dissection preserving perforators, and tension-free inset — followed by diligent vascular monitoring postoperatively.
Fasciocutaneous flaps are based on the rich vascular plexuses located above and below the deep fascia, which allow for thin, pliable tissue transfer with reliable perfusion. They remain a reliable and versatile option, particularly for salvage reconstructions where simpler techniques are preferred (Kovar, 2020).
Fasciocutaneous Flap Design
Flap success begins before the incision. Detailed design, proper patient positioning, and vascular assessment are essential to avoid intraoperative surprises. Key principles of fasciocutaneous flap design includes,
- Deep Fascia Inclusion: Incorporating deep fascia strengthens vascularity and increases the safe length-to-width ratio.
- Perforator-Based Planning: Doppler identification of dominant perforators enhances design precision and outcomes.
- Flap Sizing and Design: Precisely match the defect while accounting for length lost during rotation. Use these approximations for rotational loss: 45° = 5% loss, 90° = 15% loss, 180° = 40% loss
- Flap Delay Technique: Pre-elevation of the flap can increase vascular territory before transfer.
“The Doppler doesn’t lie!” Preoperative Doppler mapping significantly reduces intraoperative uncertainty and flap failure.
Fasciocutaneous Flap Elevation
The surgical steps for harvesting and insetting a fasciocutaneous flap emphasise vascular preservation and a tension-free closure.
Step 1: Incision and Flap Elevation
- Incise through the skin, subcutaneous fat, and deep fascia.
- Elevate the flap in a subfascial plane to protect the underlying perforators.
Step 2: Pedicle Management
- Avoid skeletonising vessels unnecessarily; maintain surrounding tissues to preserve flow.
- Maintain pedicle length to allow tension-free movement to the defect.
Step 3: Flap Transfer and Inset
- Prepare the recipient site by excising nonviable tissue and undermining wound edges.
- Rotate or advance the flap into position without kinking the pedicle.
- Suture fascia to fascia for structural stability, using minimal tacking sutures on the skin.
The following video is an example of a PIA fasciocutaneous flap.
PIA Fasciocutaneous Flap
Postoperative Care and Monitoring
Immediate postoperative care focuses on early detection of vascular compromise and ensuring optimal perfusion to the transferred tissue.
Flap Monitoring
- Check for color, capillary refill, turgor, and Doppler signals regularly in the first 48–72 hours.
- Any signs of congestion or pallor should prompt rapid intervention.
Positioning and Support
- Elevate extremities to reduce edema.
- Avoid compression over the flap or pedicle to prevent venous outflow obstruction.
Reassessment for Secondary Grafting
- In thinner flaps with volume loss, skin grafting may be required for final contouring.
Fascial and adipofascial flaps are skinless variants, relying on fascia alone or fascia with fat for vascularised reconstruction.
Complications of Fasciocutaneous Flaps
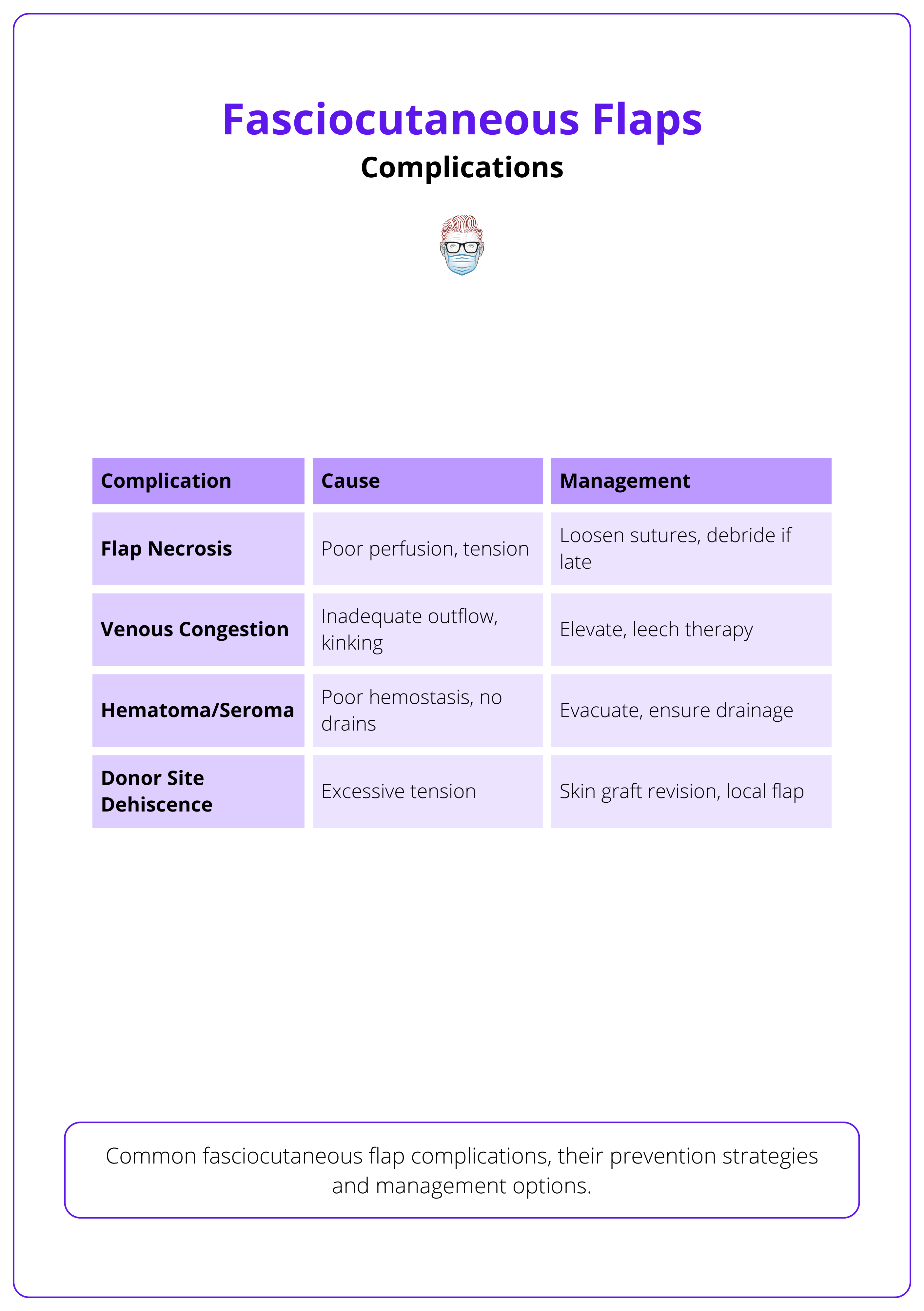
Fasciocutaneous flaps are generally safe and effective, but complications such as necrosis, venous congestion, and donor site issues can occur — most often due to vascular compromise, tension, or poor intraoperative handling.
The viability of fasciocutaneous flaps hinges on perfusion through delicate perforator networks. Disruption to either arterial inflow or venous outflow can threaten flap survival.
Flap Necrosis (Partial or Total)
- Cause: Inadequate vascular supply, excessive tension, or pedicle compromise.
- Clinical Signs: Dusky color, reduced capillary refill, distal tip ischemia.
- Tip: Always include the deep fascia in flap elevation and avoid over-tightening sutures—these can compress perforators and lead to distal necrosis (Tolhurst, 1986).
Venous Congestion
- Cause: Twisted pedicle, excessive flap rotation, or tight closure restricting venous drainage.
- Signs: Flap appears bluish or congested with rapid capillary refill and increased turgor.
- Tip: Limit rotation angles and avoid kinking the pedicle. Elevate the limb postoperatively to promote venous return.
Arterial Insufficiency
- Cause: Pedicle tension, inadequate perforator inclusion, or compression.
- Signs: Pale, cool flap with delayed capillary refill and absent Doppler signal.
- Tip: Map perforators with a handheld Doppler during planning and preserve pedicle soft tissue during elevation.
Hematoma and Seroma Formation
- Cause: Incomplete hemostasis or failure to place suction drains.
- Complications: Flap elevation, wound tension, delayed healing, secondary infection.
- Tip: Perform meticulous hemostasis and always use drains for large or high-risk flaps. Avoid early removal if drainage persists.
Infection and Wound Breakdown
- Cause: Hematoma, poor flap perfusion, or contaminated wounds.
- Risk Factors: Diabetes, smoking, peripheral vascular disease, or late presentation.
- Signs: Erythema, discharge, wound dehiscence, or flap edge necrosis.
- Tip: Minimise dead space, ensure tension-free closure, and avoid using compromised tissue for inset.
Donor Site Dehiscence or Graft Loss (if used)
- Cause: Closure under tension or poor vascularity at the donor site, poor bed preparation, shearing forces, or infection.
- Tip: If tension is unavoidable, opt for split-thickness skin grafts (STSGs) over forced primary closure to prevent breakdown. Reinforce with bolster dressings and delay grafting if bed viability is questionable.
Contour Defects & Aesthetic Concerns
- Cause: Loss of subcutaneous bulk or irregular wound bed topography.
- Outcome: Visible depressions or asymmetry, especially in cosmetic zones.
- Tip: Choose donor sites with good tissue match and anticipate visible defects in thin-skinned areas like the forearm.
The complications of fasciocutaneous flaps are summarised below.
Avoid excessive tension at closure as over-tightened sutures can restrict microcirculation, leading to ischemia and distal necrosis.
Advantages and Limitations of Fasciocutaneous Flaps
Fasciocutaneous flaps offer distinct benefits but also come with specific structural and practical limitations. Their use must be carefully tailored to the clinical scenario.
Advantages
- Muscle Function Preservation: These flaps spare muscle tissue, preserving strength and mobility — particularly valuable in functional areas such as the lower limb. This also reduces donor site morbidity compared to muscle-based flaps.
- Thin and Pliable Tissue: Their soft, flexible nature makes them ideal for reconstructing contour-sensitive areas like the hand, face, and distal lower limb. Unlike bulkier muscle flaps, they provide superior aesthetic outcomes.
- Potential for Sensory Restoration: When incorporating cutaneous nerves, fasciocutaneous flaps can restore sensation — especially beneficial in the hand and foot where tactile feedback is crucial.
Limitations
- Limited Reach in Pedicled Designs: Pedicle length and arc of rotation restrict the flap’s reach, particularly in pedicled designs.
- Tip: Consider converting to a free flap if the arc is insufficient or there's a risk of vascular compromise due to tension.
- Unsuitable for Deep or Voluminous Defects: These flaps lack bulk, making them less effective for filling large cavities or obliterating dead space.
- Alternative: Muscle flaps provide superior volume and are more effective in managing deep infections.
- May Require Delayed Flap Technique: In areas with marginal vascularity — such as distal limbs — a staged delay procedure may be necessary to improve perfusion before full elevation.
- Guidance: Plan delays proactively when vascular supply is uncertain.
- Donor Site Morbidity: Large flaps can lead to delayed healing or contour irregularities at the donor site. Closure may require additional interventions like skin grafting.
- Frequent Need for Skin Grafting: When primary closure isn’t possible, split-thickness skin grafts (STSGs) are often required. This can result in color or texture mismatch between donor and recipient sites.
- Historically Considered Less Infection-Resistant: While once thought to be less vascularised than muscle flaps, newer evidence suggests fasciocutaneous flaps can perform comparably in managing infections in selected cases.
Conclusion
1. Overview: Fasciocutaneous flaps consist of skin, subcutaneous fat, and deep fascia, providing thin, pliable coverage while preserving muscle function. Used in trauma, oncologic reconstruction, and pressure sores.
2. Anatomy & Physiology: Perfusion relies on fasciocutaneous perforators (musculocutaneous, septocutaneous, and direct cutaneous) and suprafascial/subfascial plexuses, ensuring vascular reliability.
3. Classification & Design: Cormack & Lamberty (Types A–D) categorises fasciocutaneous flaps by vascular supply patterns. Mathes & Nahai (Types A–C) is based on pedicle type and blood supply source.
4. Comparison: Fasciocutaneous flaps for contour-sensitive coverage, muscle flaps for bulk & deep defects.
5. Surgical Technique & Post-op: Pre-op: Precise flap planning to match the defect and minimise tension. Intra-op: Subfascial dissection to preserve perforators and avoid vascular compromise. Post-op: Monitor for vascular integrity, edema control, and donor site healing.
6. Complications & Management: Common risks: Necrosis, venous congestion, hematoma, infection, and donor site morbidity. Prevention: Proper flap design, tension-free inset, and vascular monitoring.
Further Reading
- Pontén B. The fasciocutaneous flap: its use in soft tissue defects of the lower leg. Br J Plast Surg. 1981;34(2):215-220. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(81)80097-5
- Cormack GC, Lamberty BG. Fasciocutaneous vessels: their distribution on the trunk and limbs, and their clinical application in tissue transfer. Anat Clin. 1984;6(2):121-131. doi:10.1007/BF01773164
- Hallock GG. Local fasciocutaneous flaps for cutaneous coverage of lower extremity wounds. J Trauma. 1989;29(9):1240-1244. doi:10.1097/00005373-198909000-00010
- Fix RJ, Vasconez LO. Fasciocutaneous flaps in reconstruction of the lower extremity. Clin Plast Surg. 1991;18(3):571-582. PMID:1889167
- Losco L, Sereni S, Aksoyler D, et al. Perforator-based adipofascial flaps and ADM: a novel combined approach to distal lower extremity defects. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022;10(2):e4131. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000004131
- AlMugaren FM, Pak CJ, Suh HP, Hong JP. Best local flaps for lower extremity reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020;8(4):e2774. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002774
- Gupta S, Gupta P, Khichar P, Mohammad A, Escandón JM, Kalra S. Perforator propeller flaps for lower extremity soft-tissue defect reconstruction: shortening the learning curve. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2022;27:101831. doi:10.1016/j.jcot.2022.101831
- Vogt PM, Limbourg FP. A new fasciocutaneous flap model identifies a critical role for endothelial Notch signaling in wound healing and flap survival. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):12542. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-39561-9
- Boretto J, Morgan B. Fasciocutaneous flaps. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. PMID:32965937
- Tolhurst DE. Clinical experience and complications with fasciocutaneous flaps. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986;20(1):75-78. doi:10.3109/02844318609006296


