5 Key Points
- Uncommon lymphoma linked to textured, high surface grade, implants.
- Incidence is increasing as awareness increases.
- Late-onset seromas should be urgently investigated with cytology and histology.
- Tumour Markers are CD30+ and ALK-
- Early stage disease is curable with surgery alone.
Define
Breast implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (Bi-ALCL) is a CD30+, ALK-, T-cell derived lymphoma. It fits within the non-Hodgkin lymphoma group and is linked to textured breast implants.
Pathogenesis
A unifying hypothesis of published literature suggests textured implants with a high surface grade, bacterial contamination, inflammation and patient susceptibility interact over time to produce T-cell transformation. It is multifactorial, like most carcinogenesis
More specifically:
- Textured implants creates inflammation from friction
- High surface grade acts as passive conduit for bacterial proliferation
- Bacterial contamination is a form of microbiome induction that potentiates carcinogenesis. This is suggested by cluster patterns of incidence, biofilm formation and growth of both gram-positive and negative organisms.
Incidence
Wide variations in published data from 1 in 3,000 to 1 in 3,000,000. This variation is due to geographic discrepancies in databases and the different type of textured implants available. Importantly, the incidence is increasing each year.
Clinical Picture
History and Examination
- Insidious onset
- Late onset seroma (>1 year post implant), most commonly 8 years after implants inserted.
- Firm mass and lymphadenopathy (advanced disease)
- Capsular contracture (non-specific)
Risk Factors
- Textured Implants (no reports of link to smooth implants), particularly those with high surface grade classification (large surface area and rough)
- Immunocompromised patient

Investigations
A multi-disciplinary approach is needed between surgeon, histology, radiology and, if diagnosed, oncology teams.
Seroma
A pre-operative Ultrasound-guided seroma aspirate should be investigated for
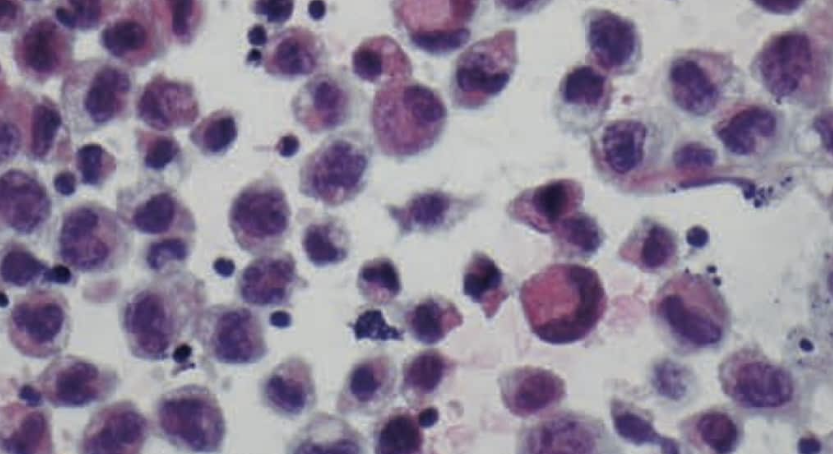
- Cytology: large anaplastic cells
- Flow cytometry: aberrant T-Calls
- Immunohistochemistry: CD30+ and ALK- makers.
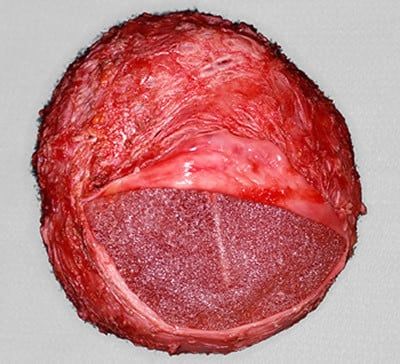
Histology
Intra-operative specimens of any residual seroma and the implant capsule should be sent at the time of capsulectomy.
The absence of tumour cells following a positive seroma aspiration does not suggestion regression or resolution, but rather a lowering of the tumour cell burden following the drainage of the malignant seroma.
Microbiology
This does not assist in diagnosing or staging but it is interesting to note the growth of both gram-positive and negative bacteria. This is different to capsular contracture pathophysiology, which mainly grows solely gram-positive bacteria.
Staging
The aim of the investigations to diagnose and appropriately stage the patient.
| Stage | Pathology | Incidence |
| IA (negative) | Seroma Positive, Capsule Negative | 63% |
| IA (positive) | Seroma Positive, Luminal Capsule Positive | 16% |
| IC | Capsule infiltrated | 7% |
| IIA | Mass extending beyond Capsule | 11% |
| III | Metastatic disease with 1 axillary node | 1% |
| III | Metastatic disease with multiple nodes | 1% |
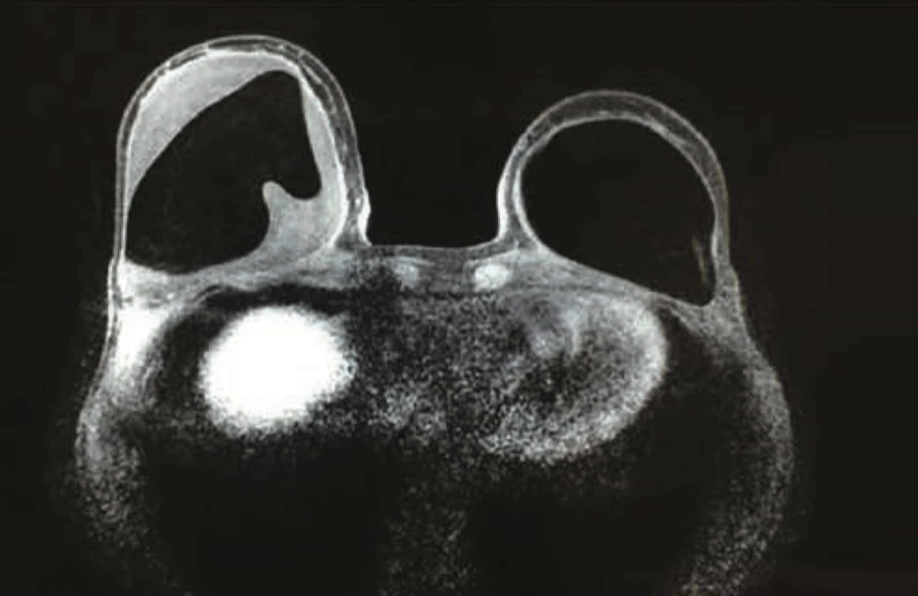
Radiology
There are no standardised guidelines referencing the role of further radiology investigations. This should be considered as a case-by-case basis in addition to the ultrasound for guided seroma aspiration.

Management
Pre-Diagnosis
Management of this condition begins in the pre-operative setting by ensuring the patient has received informed consent and they understand the risk of Bi-ALCL
Intra-operatively, efforts should be focused on disease prevention through implant choice and reducing implant contamination.
Post-Diagnosis
Early recognition is key. Following the diagnosis, staging and multi-disciplinary team input, surgery is next.
Options to consider:
- Open Capsulectomy of anterior and/or posterior wall
- Implant replacement with a smooth implant
Surgical treatment of Bi-ALCL. Courtesy of Dr Tim Papadopoulos
Stage 1A is indolent and curable through surgery alone.
Recent publications have suggested a screening programme, but this has not been formally introduced.


